ニュース
グローバルセキュリティメーカーの株式会社サイバーセキュリティクラウド(本社:東京都品川区、代表取締役社長 兼 CEO:小池敏弘、以下「当社」)は、2025年7月1日~9月30日を対象とした『Webアプリケーションへのサイバー攻撃検知レポート(以下「本レポート」)』を発表します。本レポートは、当社が提供するWebアプリケーションへのサイバー攻撃を可視化・遮断するクラウド型WAFの『攻撃遮断くん』、及びパブリッククラウドWAFの自動運用サービス『WafCharm(ワフチャーム)』で観測したサイバー攻撃ログを集約し、分析・算出しています。
≪レポートサマリー≫
・2025年7月~9月の3ヵ月で5億件を超える攻撃を検知
・クラウド連携経路を狙う攻撃が前年比約13.6倍に拡大
・7月下旬に大規模な攻撃スパイクを観測し、検知数は平常時の最大50倍に
■ 全体概要:5億件超の攻撃を検知
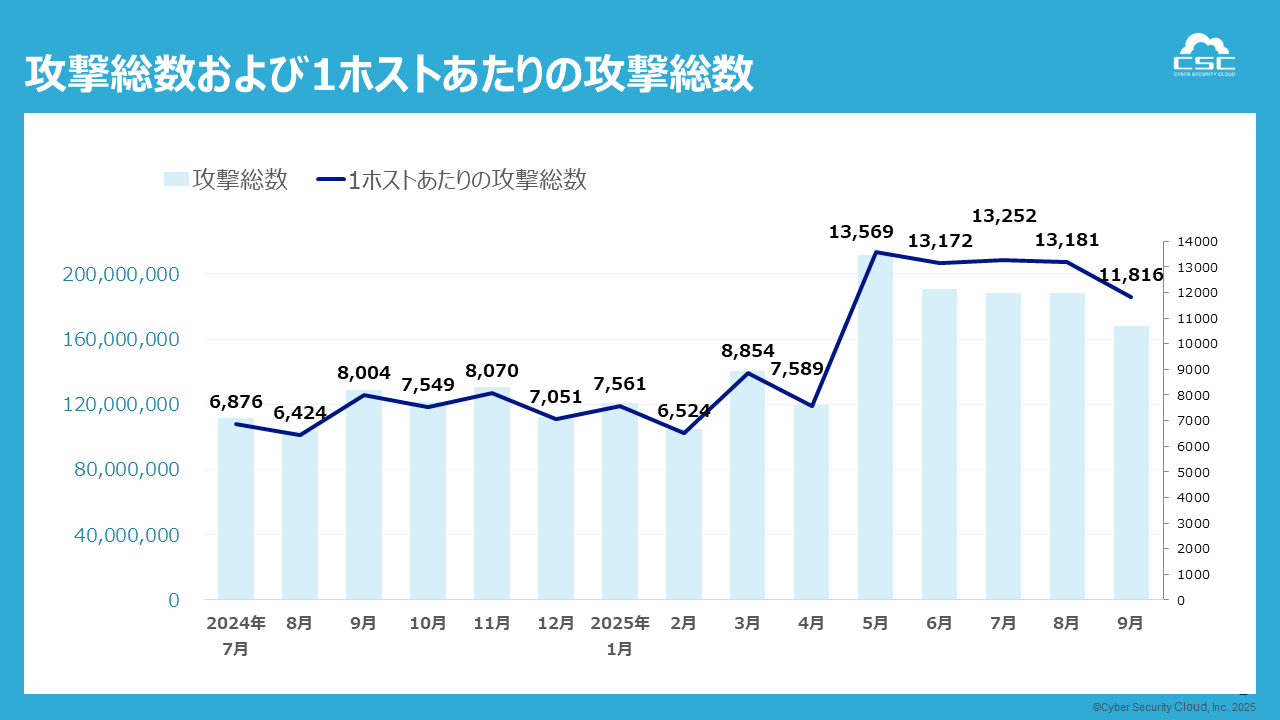
2025年7月〜9月の期間に観測された攻撃検知件数は、合計約5億4,400万件となりました。
月別推移を見ると、7月以前から高水準で推移し、9月にやや減少したものの、大量の攻撃が継続的に観測されています。
さらに、1ホスト※1あたりの攻撃件数は前年比で約2倍に増加しました。
※1 『攻撃遮断くん』の保護対象ホスト数(Webタイプ:FQDN数、サーバタイプ:IP数)と、『WafCharm』の保護対象ホスト数(WebACL)との総数を分母に概算。
■ 攻撃種別の構成比と傾向
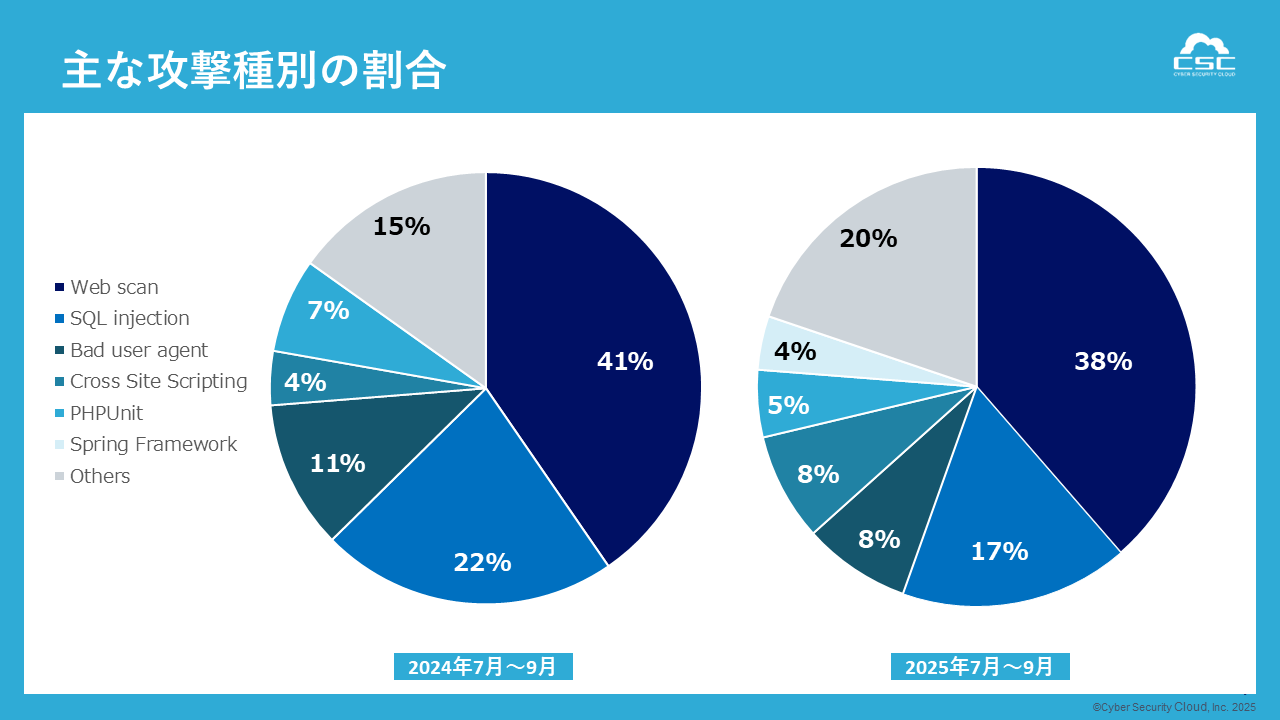
今回の調査期間における主な攻撃種別の傾向を見ると、総攻撃数は増加しましたが、攻撃種別構成に大きな変化は見られませんでした。
本レポートでは、SQLインジェクション(SQLi)やクロスサイトスクリプティング(XSS)など、従来型のWebアプリケーション攻撃が引き続き高頻度で観測されました。これらの攻撃手法は長年にわたり主要な脅威であり続けていますが、近年では攻撃の自動化や大規模化が進行しており、検知件数ベースでは過去最高水準に達しています。特に、入力値の検証が不十分なWebアプリケーションや、設定ミス・アクセス制御の不備といった構成上の問題は、セキュリティホールのリスクがあり、攻撃の足がかりとなる可能性があります。
■クラウド連携経路を狙う攻撃が前年比約13.6倍に拡大
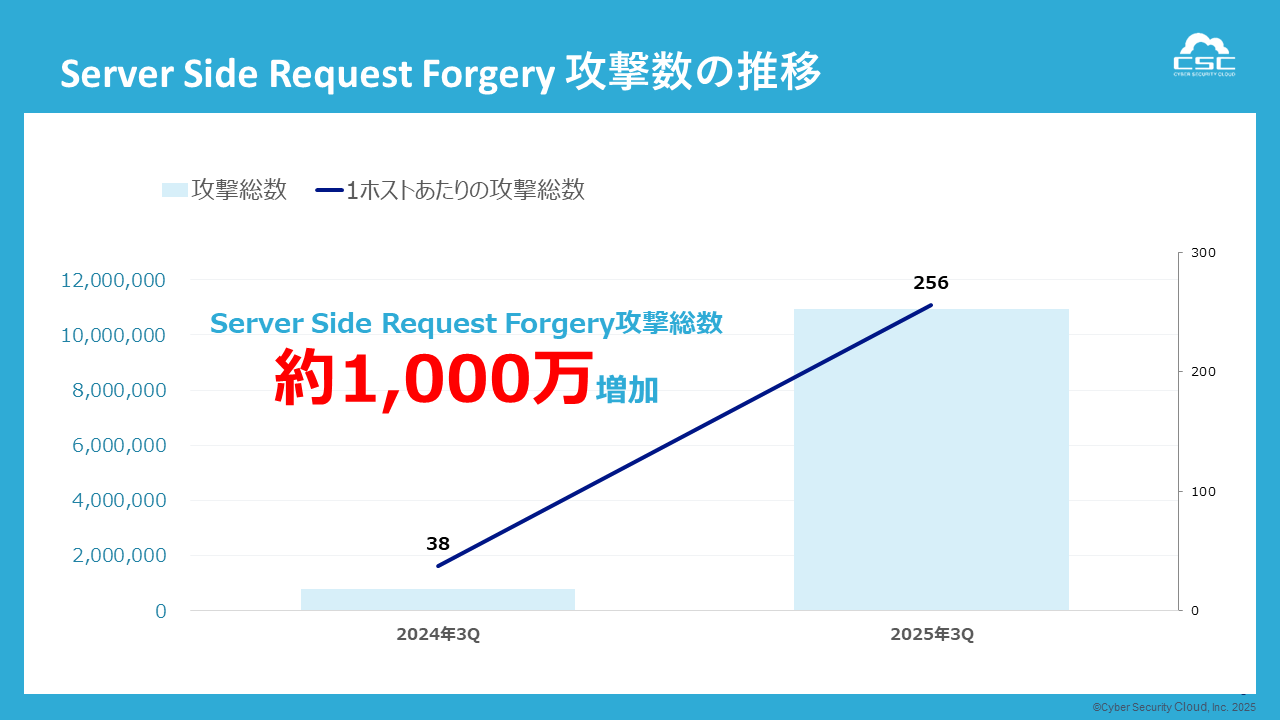
2025年第3四半期(7〜9月)に観測された Server Side Request Forgery(SSRF) による検知件数は、約1,094万件と前年同期(2024年3Q:80万件)から約13.6倍の急増を記録しました。
アプリケーションが外部リクエストを行う処理に悪意ある入力を利用して内部サーバやクラウドメタデータサービスへの不正アクセスを誘発する攻撃です。クラウド化やマイクロサービスの普及に伴い、攻撃対象領域が急速に拡大しています。
7月下旬から9月上旬にかけてSSRF関連トラフィックが顕著に増加。発信元は複数国に分散しており、ボットネットによる自動スキャンやAPI経路を悪用した情報収集型攻撃の特徴を示しています。また、SSRFの増加はWeb攻撃全体の増加と連動しており、Traversal攻撃やXML External Entity(XXE)攻撃と同様に、API層やデータ交換層を標的とする攻撃グループの活動が活発化していることが確認されました。
この動きの背景には、クラウド環境でのサービス連携の複雑化と、開発現場での内部APIやメタデータエンドポイントの露出が挙げられます。設定ミスや権限緩和など、わずかな構成上の不備が攻撃経路として悪用されるケースが増えています。
クラウド環境でSSRF攻撃が成功した場合の被害の例として、攻撃者はクラウド環境内のメタデータAPIにアクセスし、認証情報の取得や内部ネットワーク経由の横展開を実施できる可能性があります。結果として、サービスアカウントの乗っ取りや機密データの漏えいといった深刻な被害につながるリスクが高まっています。
■ 攻撃発信元の傾向
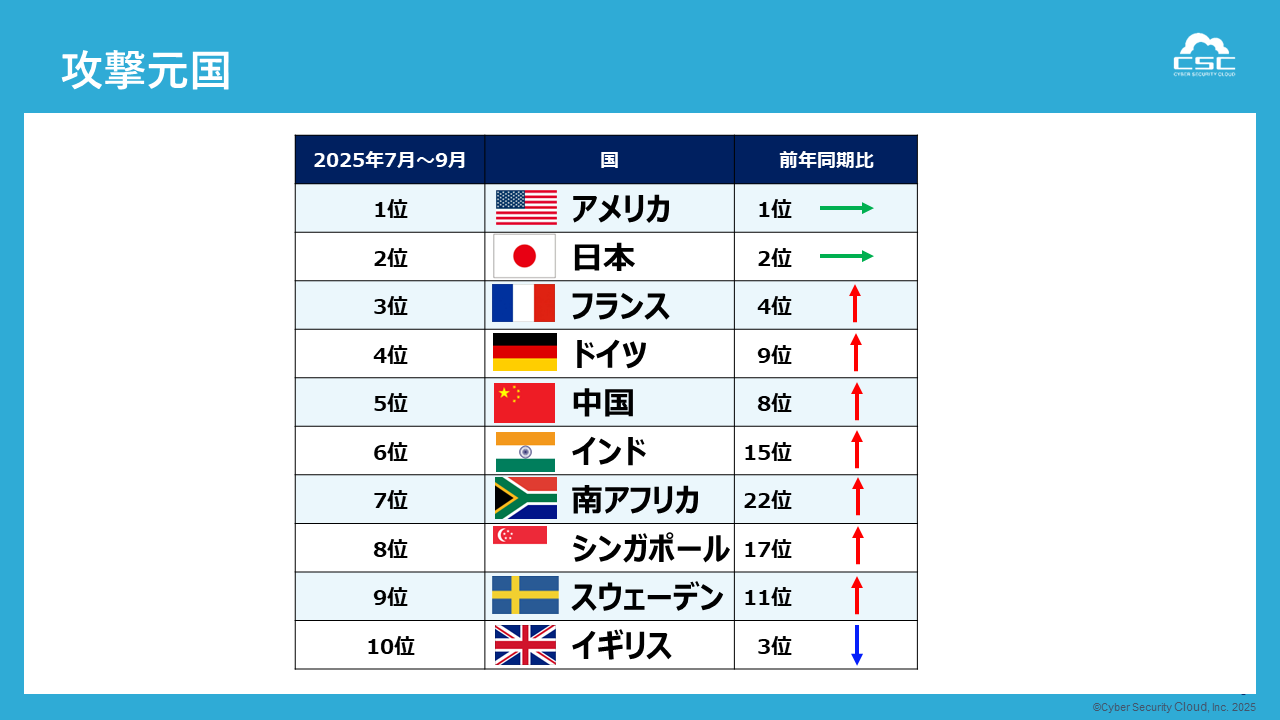
攻撃の発信元IPアドレスを国別に分類したところ、米国からのアクセスが全体の約半数を占め最多となりました。次いで日本・フランス・ドイツ・中国の順で上位を形成しており、北米・欧州・アジアの三極構造が引き続き顕著です。
■ 異常検知分析
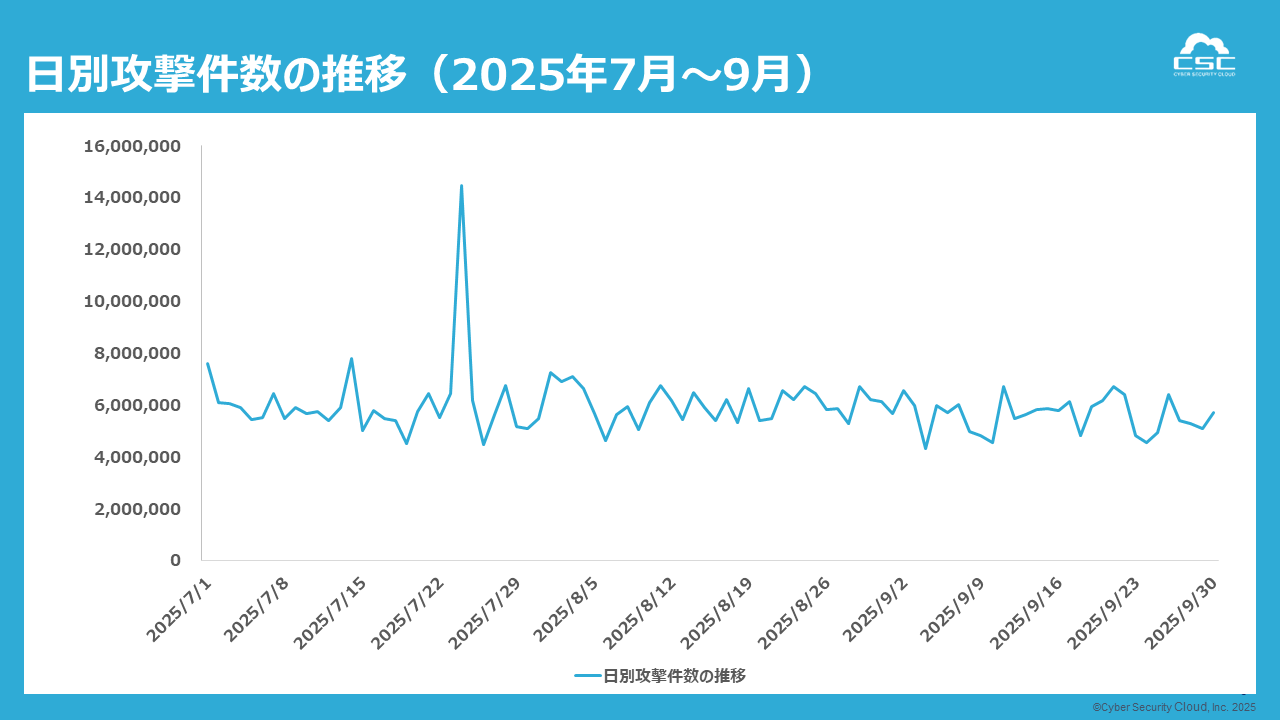
2025年7月下旬に、通常を大きく上回る攻撃の増加が確認されました。
この期間には、SQLインジェクションやクロスサイトスクリプティング(XSS)など、複数の攻撃手法が同じ時期に集中して発生しており、自動化された攻撃キャンペーンが展開されていた可能性が高いと見られます。
特に7月23日から24日にかけては、複数の攻撃ルールで平常時の数十倍から数百倍に相当する検知数が記録されました。
これらの攻撃は、特定の企業やシステムを狙ったものではなく、世界的に展開された無差別型の大規模スキャン攻撃であると考えられます。攻撃の内容を分析すると、WebフォームやURLパラメータなどを通じて、脆弱なアプリケーションを探し出そうとする動きが顕著でした。
また、攻撃に使用されたリクエストの多くは自動生成された文字列や連番のURL構造を持っており、手動ではなくボットやスクリプトによって一斉に送信されたものと推測されます。
さらに、7月の急増以降も8月〜9月にかけて小規模な攻撃の波が断続的に発生しており、単発的な試行ではなく、長期間にわたる探索型の攻撃活動であることがうかがえます。特にSQLインジェクション関連では、システム内部の情報やデータベース構造を特定する試みが繰り返し行われていました。
このような攻撃は、クラウド環境や公開APIなど、多くの企業が利用するサービスにも影響を及ぼす可能性があり、異常なリクエスト集中を早期に検知・遮断できる監視体制の強化が今後ますます重要になるといえます。
■ 株式会社サイバーセキュリティクラウド 代表取締役CTO 渡辺 洋司からのコメント
2025年第3四半期も、国内外を問わずWebアプリケーション層を狙った攻撃が継続的に観測されました。特に、クラウド連携経路を狙う Server Side Request Forgery(SSRF)攻撃 の急増は象徴的であり、クラウドやAPIといった開発環境が新たな攻撃対象として注目されていることを示しています。
また、7月下旬にはSQLインジェクションやXSSといった従来的な攻撃手法が同時多発的に観測され、自動化されたスキャン型攻撃が世界規模で行われていたことが明らかになりました。これは単なる一過性の現象ではなく、攻撃者がAIや自動化ツールを駆使し、より短期間で多様な手法を組み合わせるようになっていることを示唆しています。
攻撃が進化を続ける一方で、防御側も同様に自動化・高度化を進める必要があります。当社では、WAF製品における検知ルールのリアルタイム最適化やクラウド構成に応じた防御自動化を強化し、企業が「安心安全にクラウドを使いこなせる」環境を継続的に支援してまいります。
サイバー攻撃はもはや特定業界の問題ではなく、すべてのデジタルサービスに共通する社会的課題です。セキュリティを“後付け”ではなく“設計段階からの前提”として捉える文化の普及を、これからも私たちが牽引していきます。
■株式会社サイバーセキュリティクラウドについて
会社名:株式会社サイバーセキュリティクラウド
所在地:〒141-0021 東京都品川区上大崎3-1-1 JR東急目黒ビル13階
代表者:代表取締役社長 兼 CEO 小池敏弘
設立:2010年8月
URL:https://www.cscloud.co.jp
「世界中の人々が安心安全に使えるサイバー空間を創造する」をミッションに掲げ、世界有数のサイバー脅威インテリジェンスを駆使したWebアプリケーションのセキュリティサービスを軸に、脆弱性情報収集・管理ツールやクラウド環境のフルマネージドセキュリティサービスを提供している日本発のセキュリティメーカーです。私たちはサイバーセキュリティにおけるグローバルカンパニーの1つとして、サイバーセキュリティに関する社会課題を解決し、社会への付加価値提供に貢献してまいります。
